目录
目录
CSS布局
常见布局(PC)
- 固定宽度布局
- 弹性(fluid)布局
- 响应式布局 —— 多终端(PC、Pad、Phone)
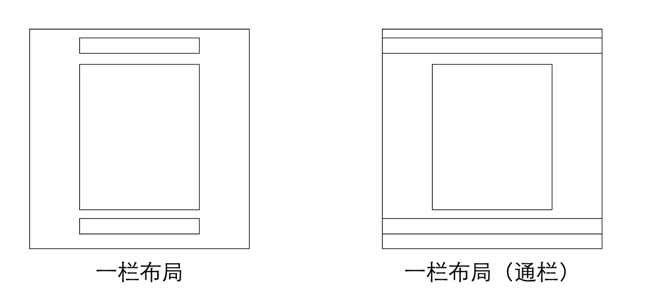
单列布局
如何实现
定宽
width: 1000px; 或 max-width: 1000px;
水平居中
margin-left: auto; margin-right: auto;
范例
范例
注意 max-width和width的区别
<style>
.layout{
/* width: 960px; */
max-width: 960px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
#header{
height: 60px;
background: red;
}
#content{
height: 400px;
background: blue;
}
#footer{
height: 50px;
background: yellow;
}
</style>
<div class="layout">
<div id="header">头部</div>
<div id="content">内容</div>
<div id="footer">尾部</div>
</div>
进化
省标签,便于控制局部 范例
<style>
.layout{
width: 960px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
#header{
height: 60px;
background: red;
}
#content{
height: 400px;
background: blue;
}
#footer{
height: 50px;
background: yellow;
}
</style>
<div id="header" class="layout">头部</div>
<div id="content" class="layout">内容</div>
<div id="footer" class="layout">尾部</div>
通栏
给通栏加背景色 范例
<style>
.layout{
width: 960px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
#header{
height: 60px;
background: red;
}
#content{
height: 400px;
background: blue;
}
#footer{
height: 50px;
background: yellow;
}
</style>
<div id="header">
<div class="layout">头部</div>
</div>
<div id="content" class="layout">内容</div>
<div id="footer">
<div class="layout">尾部</div>
</div>
查看范例效果,能发现不完美的地方吗?
通栏优化
给 body 设置min-width 去掉滚动背景色 bug
<style>
.layout{
width: 960px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
body{
min-width: 960px;
}
#header{
height: 60px;
background: red;
}
#content{
height: 400px;
background: blue;
}
#footer{
height: 50px;
background: yellow;
}
</style>
<div id="header">
<div class="layout">头部</div>
</div>
<div id="content" class="layout">内容</div>
<div id="footer">
<div class="layout">尾部</div>
</div>
内部元素水平居中
.parent{text-align:center;}
.child{display: inline-block;}
IE 6 不支持 inline-block (为什么用下面的写法)
.child{*display: inline; *zoom: 1;}
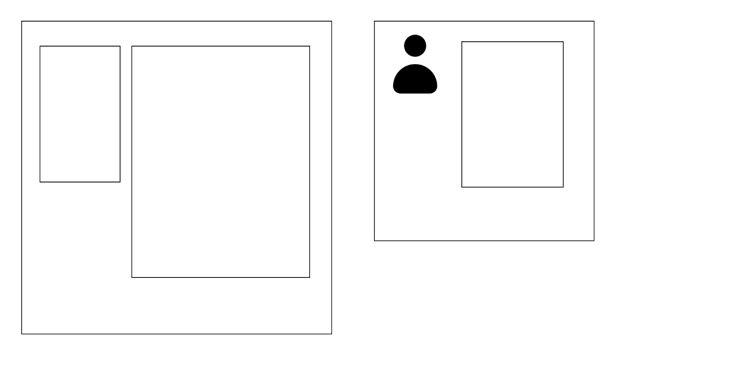
双列布局
一列固定宽度,另外一列自适应宽度
如何实现
浮动元素 + 普通元素margin 范例
<style>
#content:after{
content: '';
display: block;
clear: both;
}
.aside{
width: 200px;
height: 500px;
background: yellow;
float: left;
}
.main{
margin-left: 210px;
height: 400px;
background: red;
}
#footer{
background: #ccc;
}
</style>
<div id="content">
<div class="aside">aside</div>
<div class="main">content</div>
</div>
<div id="footer">footer</div>
如果侧边栏在右边呢?
侧边栏在右
谨记页面元素的渲染顺序 范例
<style>
#content:after{
content: '';
display: block;
clear: both;
}
.aside{
width: 200px;
height: 500px;
background: yellow;
float: right;
}
.main{
margin-right: 210px;
height: 400px;
background: red;
}
#footer{
background: #ccc;
}
</style>
<div id="content">
<div class="aside">aside</div>
<div class="main">content</div>
</div>
<div id="footer">footer</div>
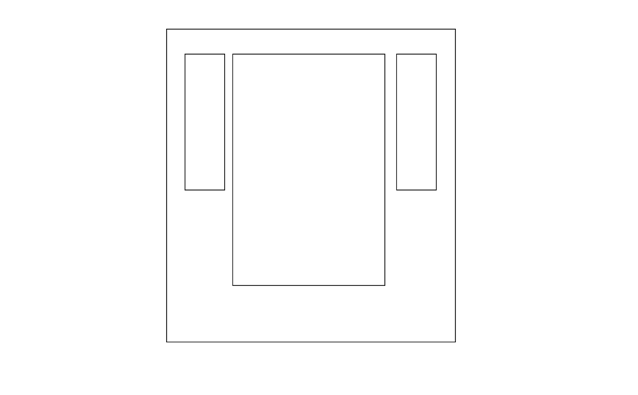
三列布局
两侧两列固定宽度,中间列自适应宽度
如何实现
#content:after{
content: '';
display: block;
clear: both;
}
.menu{
width: 100px;
height: 500px;
background: pink;
float: left;
}
.aside{
width: 200px;
height: 500px;
background: yellow;
float: right;
}
.main{
margin-left: 110px; /*为什么要加margin-left*/
margin-right: 210px;
height: 400px;
background: red;
}
#footer{
background: #ccc;
}
<div id="content">
<!-- 为什么不是main在前面 -->
<div class="menu">aside</div>
<div class="aside">aside</div>
<div class="main">content</div>
</div>
<div id="footer">footer</div>
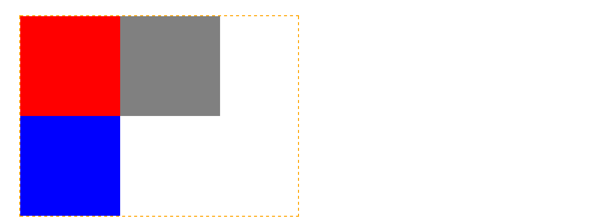
浮动 vs 负margin
对于相邻的两个浮动元素,如果因为空间不够导致第二个浮动元素下移,可以通过给第二个浮动元素设置 margin-left: 负值 来让第二个元素上移,其中 负值 大于等于元素上移后和第一个元素重合的临界值
三个浮动元素
最后一个浮动元素使用了负边距
范例演示
范例 想想最后一个元素为什么要设置为 -20px?
.float{
overflow:hidden;
width:280px;
border:dashed 1px orange;
}
.float .item{
width:100px;
height:100px;
float:left;
}
.float .item:nth-child(1){
background:red;
}
.float .item:nth-child(2){
background:grey;
}
.float .item:nth-child(3){
background:blue;
margin-left: -20px; /* 为什么这里是 -20px ??*/
}
</style>
<div class="float">
<div class="item"></div>
<div class="item"></div>
<div class="item"></div>
</div>
水平等距排列
<style>
ul,li{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
list-style: none;
}
.ct{
overflow:hidden;
width: 640px;
border:dashed 1px orange;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.ct .item{
float:left;
margin-left: 20px;
margin-top: 20px;
width:200px;
height:200px;
background: red;
}
.ct>ul{
margin-left: -20px;
}
</style>
<div class="ct">
<ul>
<li class="item">1</li>
<li class="item">2</li>
<li class="item">3</li>
<li class="item">4</li>
<li class="item">5</li>
<li class="item">6</li>
<li class="item">7</li>
<li class="item">8</li>
</ul>
</div>
圣杯布局
why it?
- 是三列布局,两边固定宽度,中间自适应
- 中间内容元素在 dom 元素次序中优先位置
实现
按照注释编号,一行行实现观察效果 范例
<style>
#content:after{
content: ''; /*8*/
display: block; /*8*/
clear: both; /*8*/
}
#content{
padding-left: 100px; /*5*/
padding-right: 150px; /*5*/
}
.aside, .main, .extra{
float: left; /*2*/
}
.aside{
width: 100px; /*1*/
height: 300px; /*1*/
background: red; /*1*/
margin-left: -100%; /*4*/
position: relative; /*6*/
left: -100px; /*6*/
}
.extra{
width: 150px; /*1*/
height: 300px; /*1*/
background: yellow; /*1*/
margin-left: -150px; /*5*/
position: relative; /*7*/
left: 150px; /*7*/
}
.main{
height: 350px; /*1*/
background: blue; /*1*/
width: 100%; /*3*/
}
</style>
<div id="content">
<div class="main">main</div>
<div class="aside">aside</div>
<div class="extra">extra</div>
</div>
缺点
.mian的最小宽度不能小于.aside的宽度
why?
双飞翼布局
按照注释编号,一行行实现观察效果 范例
解决了什么问题?
<style>
#content:after{
content: ''; /*8*/
display: block; /*8*/
clear: both; /*8*/
}
#content{
}
.aside, .main, .extra{
float: left; /*2*/
}
.aside{
width: 100px; /*1*/
height: 300px; /*1*/
background: red; /*1*/
margin-left: -100%; /*4*/
}
.extra{
width: 150px; /*1*/
height: 300px; /*1*/
background: yellow; /*1*/
margin-left: -150px; /*5*/
}
.main{
/* background: blue; */ /*第1步添加,第7步注释掉*/
/* height: 350px; */ /*第1步添加,第7步注释掉*/
width: 100%; /*3*/
}
.wrap{
margin-left: 100px; /*6*/
margin-right: 150px; /*6*/
background: blue; /*7*/
height: 350px; /*7*/
}
</style>
<div id="content">
<div class="main">
<div class="wrap">main</div>
</div>
<div class="aside">aside</div>
<div class="extra">extra</div>
</div>
若愚 · 2021/09/23 12:26 · 前端基础_css_布局.md.txt