数组操作(讲义)
这是《JS 深入浅出》第八课的部分讲义
今天的课的主要内容有
- 数组的七个 API
- Underscore 源码如何读(函数节流防抖、数组去重都能在源码里看到)
join
先从最简单的数组操作开始:
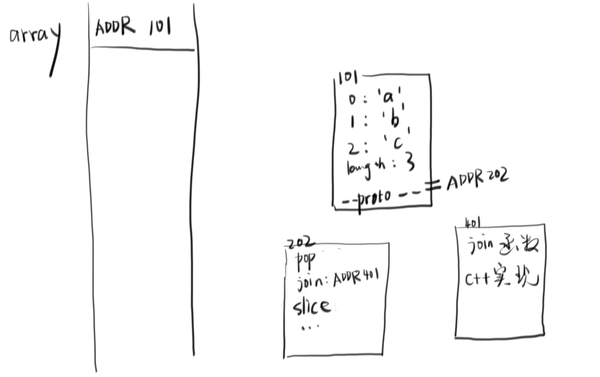
var array = ['a','b','c']
array.join('-') // 结果是 'a-b-c'
我们画一下内存图:
- array.join 实际上是 Array.prototype.join 对应的函数(array.join === Array.prototype.join === ADDR401)
- array.join('-') 等价与 array.join.call(array, '-')
- join 函数通过 this 和 arguments[0] 可以得到 array 和 '-' 两个值
所以我们可以大胆猜测 array.join 的源代码大概是这样的
Array.prototype.join = function(char){
let result = this[0] || ''
let length = this.length
for(let i=1; i< length; i++){
result += char + this[i]
}
return result
}
this 就是 array,因为你使用 array.join('-') 来调用 join 的(隐式指定this)
slice
接下来研究第二个数组操作
array.slice(beginIndex, endIndex)
显而易猜,源码大概大概大概是这样的
Array.prototype.slice = function(begin, end){
let result = []
begin = begin || 0
end = end || this.length
for(let i = begin; i< end; i++){
result.push(this[i])
}
return result
}
于是很多前端用 slice 来将伪数组,转化成数组
array = Array.prototye.slice.call(arrayLike) 或者 array = [].slice.call(arrayLike)
ES 6 看不下去这种蹩脚的转化方法,出了一个新的 API
array = Array.from(arrayLike)
专门用来将伪数组转化成真数组。
P.S. 伪数组与真数组的区别就是:伪数组的原型链中没有 Array.prototype,而真数组的原型链中有 Array.prototype。因此伪数组没有 pop、join 等属性。
sort
我听说大部分的语言内置的 sort 方法都是快速排序算法。我们就简化成选择排序吧
Array.prototype.sort = function(fn){
fn = fn || (a,b)=> a-b
let roundCount = this.length - 1 // 比较的轮数
for(let i = 0; i < roundCount; i++){
let minIndex = this[i]
for(let k = i+1; k < this.length; k++){
if( fn.call(null, this[k],this[i]) < 0 ){
[ this[i], this[k] ] = [ this[k], this[i] ]
}
}
}
}
fn.call(null, this[k], this[i]) 决定了第 k 项和第 i 项的前后(大小)关系。
fn 为 (a,b) => a-b 表示啥?fn 为 (a,b) => b-a 又表示啥?
不重要,因为如果前者不符合你的需求,那么后者一定符合你的需求,你只需要试两边就知道用哪一个了。
forEach、 map、filter 和 reduce
Array.prototype.forEach = function(fn){
for(let i=0;i<this.length; i++){
if(i in this){
fn.call(undefined, this[i], i, this)
}
}
}
forEach 和 for 的区别主要有两个:
- forEach 没法 break(有些地方用 return false 表示 break)
- forEach 用到了函数,所以每次迭代都会有一个新的函数作用域;而 for 循环只有一个作用域(著名前端面试题就是考察了这个)
Array.prototype.map = function(fn){
let result = []
for(let i=0;i<this.length; i++){
if(i in this) {
result[i] = fn.call(undefined, this[i], i, this)
}
}
return result
}
map 和 forEach 功能差不多,区别只有返回值而已。
接下来是 filter
Arra.prototype.filter = function(fn){
let result = []
let temp
for(let i=0;i<this.length; i++){
if(i in this) {
if(temp = fn.call(undefined, this[i], i, this) ){
result.push(this[i])
}
}
}
return result
}
fn.call() 返回真值就 push 到返回值,没返回真值就不 push。
接下来是 reduce
Arra.prototype.reduce = function(fn, init){
let result = init
for(let i=0;i<this.length; i++){
if(i in this) {
result = fn.call(undefined, result, this[i], i, this)
}
}
return result
}
map、filter 和 reduce 的区别:
map、filter 和 reduce 的联系:
1 map 可以用 reduce 表示
array2 = array.map( (v) => v+1 )
可以写成
array2 = array.reduce( (result, v)=> {
result.push(v + 1)
return result
}, [ ] )
2 filter 可以用 reduce 表示
array2 = array.filter( (v) => v % 2 === 0 )
可以写成
array2 = array.reduce( (result, v)=> {
if(v % 2 === 0){ result.push(v) }
return result
}, [])
Underscore.js
Underscore 是一个集合操作的库(当时 JS 没有 Set,所以集合指的是数组和对象)
主要有六类 API:
- 集合 API
- 数组 API
- 对象 API
- 函数 API
- 杂项 API
- 链式操作
Underscore 源代码阅读建议
- 搜索 underscore annotated source code,点进去
- 搜索自己感兴趣的 API,如 _.uniq
- 边看文档边看代码
后面一半的讲义略,课后有两道经典面试题。
https://link.zhihu.com/?target=https%3A//xiedaimala.com/courses/24f54465-854f-4de7-9808-72a0bf5b3181
饥人谷一直致力于培养有灵魂的编程者,打造专业有爱的国内前端技术圈子。如造梦师一般帮助近千名不甘寂寞的追梦人把编程梦变为现实,他们以饥人谷为起点,足迹遍布包括facebook、阿里巴巴、百度、网易、京东、今日头条、大众美团、饿了么、ofo在内的国内外大小企业。 了解培训课程:加微信 xiedaimala03,官网:https://jirengu.com
本文作者:饥人谷方应杭老师